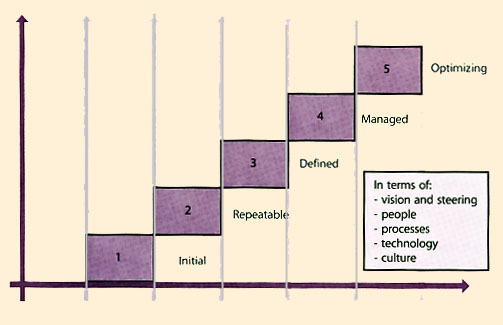
The use of the PMF in the assessment of Service Management processes relies on an appreciation of the IT Organization Growth Model. The maturity of the Service Management processes is heavily dependent on the stage of growth of the IT organization as a whole. It is difficult, if not impossible, to develop the maturity of the Service Management processes beyond the maturity and capability of the overall IT organization. The maturity of the IT organization is not just dependent on the maturity of the Service Management processes. Each level requires a change of a combination of elements in order to be fully effective. Therefore a review of processes will require an assessment to be completed against the five areas of:
These are the five areas described within the PMF for assessing process maturity. The major characteristics of each level of the PMF are as follows.

|
| Figure H. 1 Process maturity framework |
| Vision and steering | Minimal funds and resources with little activity Results temporary, not retained Sporadlc reports and reviews |
| Process | Loosely defined processes and procedures, used reactively when problems occur Totally reactive processes Irregular, unplanned activities |
| People | Loosely defined roles or responsibilities |
| Technology | Manual processes or a few specific, discrete tools (pockets/islands) |
| Culture | Tool and technology-based and driven with a strong activity focus |
| Table H.1 PMF Level 1: initial | |
| Vision and steering | No clear objectives or formal targets Funds and resources available Irregular, unplanned activities, reporting and reviews |
| Process | Defined processes and procedures Largely reactive process Irregular, unplanned activities |
| People | Self-contained roles and responsibilities |
| Technology | Many discrete tools, but a lack of control Data stored in separate locations |
| Culture | Product and service-based and driven |
| Table H.2 PMF Level 2: repeatable | |
| Vision and steering | Documented and agreed formal objectives and targets Formally published, monitored and reviewed plans Well-funded and appropriately resourced Regular, planned reporting and reviews |
| Process | Clearly defined and well-publicized processes and procedures Regular, planned activities Good documentation Occasionally proactive process |
| People | Clearly defined and agreed roles and responsibilities Formal objectives and targets Formalized process training plans |
| Technology | Continuous data collection with alarm and threshold monitoring Consolidated data retained and used for formal planning, forecasting and trending |
| Culture | Service and Customer-oriented with a formalized approach |
| Table H.3 PMF Level 3: defined | |
| Vision and steering | Clear direction with business goals, objectives and formal targets, measured
progress Effective management reports actively used Integrated process plans linked to business and IT plans Regular improvements, planned and reviewed |
| Process | Well-defined processes, procedures and standards, included in all IT staff job
descriptions Clearly defined process interfaces and dependencies Integrated Service Management and systems development processes Mainly proactive process |
| People | Inter- and intra-process team working Responsibilities clearly defined in all IT job descriptions |
| Technology | Continuous monitoring measurement, reporting and threshold alerting to a centralized set of integrated toolsets, databases and processes |
| Culture | Business focused with an understanding of the wider issues |
| Table H.4 PMF Level 4: managed | |
| Vision and steering | Integrated strategic plans inextricably linked with overall business plans, goals and
objectives Continuous monitoring, measurement, reporting alerting and reviews linked to a continual process of improvement Regular reviews and/or audits for effectiveness, efficiency and compliance |
| Process | Well-defined processes and procedures part of corporate culture Proactive and pre-emptive process |
| People | Business aligned objectives and formal targets actively monitored as part of the
everyday activity Roles and responsibilities part of an overall corporate culture |
| Technology | Well-documented overall tool architecture with complete integration in all areas of people, processes and technology |
| Culture | A continual improvement attitude, together with a strategic business focus. An understanding of the value of IT to the business and its role within the business value chain |
| Table H.5 PMF Level 5: optimizing | |
This maturity framework is aligned with the Software Engineering Institute Capability Maturity Model® Integration (SEI CMMI) and their various maturity models including the evolving CMMI-SVC, which focuses on the delivery of services.
